Bone Marrow: The Lifeline of Our Body
Bone Marrow: a soft and spongy tissue found inside bones, plays a critical role in our body’s overall health and functioning. Often overlooked, bone marrow is essential for producing blood cells that carry oxygen, fight infections, and help blood clotting. In this article, we will explore what bone marrow is, its types, functions, diseases related to bone marrow, and how bone marrow transplants can save lives.
What is Bone Marrow?
Bone marrow is the soft tissue that resides in the hollow interior of bones. It is rich in stem cells, particularly hematopoietic stem cells, which have the remarkable ability to develop into different types of blood cells. This process, known as hematopoiesis, is vital for replenishing blood cells that are constantly being used or worn out.
There are two main types of bone marrow: (Types of bone marrow)
- Red Bone Marrow: This type is responsible for producing red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red marrow is found primarily in flat bones such as the pelvis, sternum, and the ends of long bones.
- Yellow Bone Marrow: Composed mostly of fat cells, yellow bone marrow serves as a storage site for fats and plays a minor role in blood cell production. It is typically found in the central cavities of long bones. (Yellow bone marrow)
Where is bone marrow located
Bone marrow, a soft, spongy tissue, is primarily located in the hollow centers of large bones. This essential tissue can be found in the pelvic bones, ribs, vertebrae, and the ends of long bones like the femur and humerus.
Functions of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow performs several crucial functions that are indispensable for our survival:
- Blood Cell Production:
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): These cells carry oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body and return carbon dioxide to be exhaled.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs): These cells are part of the immune system and help fight infections.
- Platelets: They are responsible for blood clotting, preventing excessive bleeding when injuries occur.
- Stem Cell Production: Bone marrow houses stem cells that can transform into various cell types, ensuring the body can repair and regenerate tissues.
- Immune System Support: Bone marrow is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system by producing white blood cells that fight infections and diseases. (Bone marrow function in immune system)
Diseases Related to Bone Marrow
When bone marrow malfunctions, it can lead to a variety of serious health conditions. Some of the most common bone marrow-related diseases include:
- Leukemia: A type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, leading to the uncontrolled production of abnormal white blood cells.
- Aplastic Anemia: This condition occurs when the bone marrow fails to produce sufficient amounts of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS): These are a group of disorders caused by poorly formed or dysfunctional blood cells due to bone marrow abnormalities.
- Lymphoma: This is a type of blood cancer that starts in the lymphatic system but can spread to the bone marrow, affecting its function.
- Multiple Myeloma: A cancer of plasma cells, which are a type of white blood cell found in the bone marrow. This disease leads to bone pain, anemia, and increased susceptibility to infections.
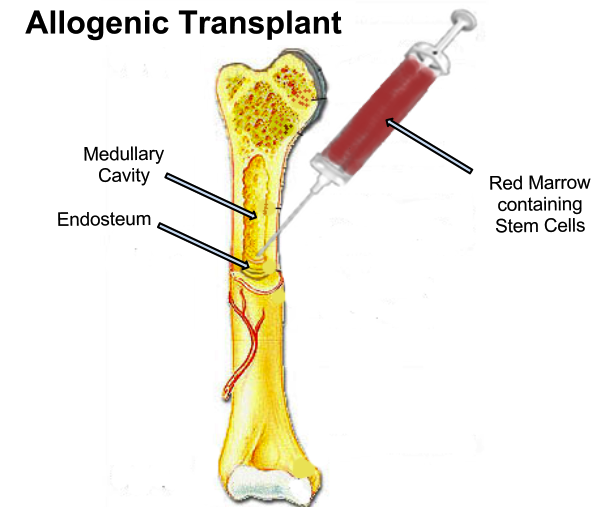
Bone Marrow Transplant: A Lifesaving Procedure
For patients suffering from severe bone marrow diseases, a bone marrow transplant (BMT) can be a lifesaving treatment. There are two main types of bone marrow transplants:
- Autologous Transplant: In this procedure, a patient’s own healthy bone marrow cells are harvested, stored, and later reinfused after intensive treatment like chemotherapy. This is often used for treating certain cancers.
- Allogeneic Transplant: Here, bone marrow cells are taken from a donor whose tissue type matches that of the patient. This is commonly used for treating blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma.
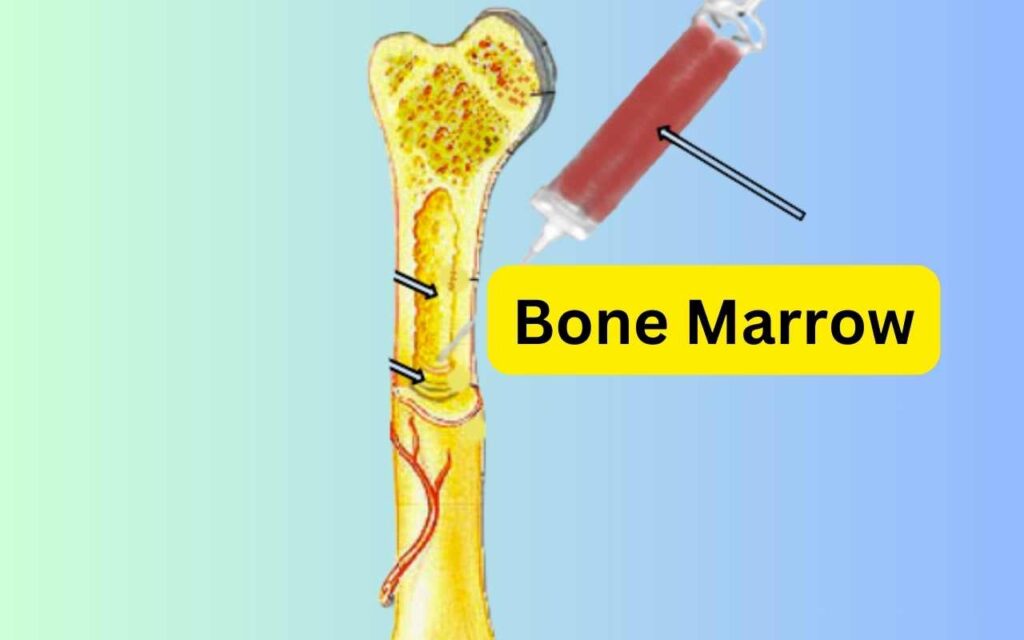
Bone marrow transplants can completely replace diseased or damaged bone marrow, allowing the body to regenerate healthy blood cells and restore the immune system. However, finding a compatible donor, especially for an allogeneic transplant, can be challenging due to the need for a close genetic match.
Recovery and Risks: Recovery can be lengthy, requiring close medical monitoring to manage potential complications like infections, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and organ damage. However, the success of a BMT can lead to remission and a significantly improved quality of life.
Stroke: Types, Causes, and Treatment
Maintaining Healthy Bone Marrow
To keep your bone marrow healthy, it is essential to follow a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly:
- Iron: Essential for red blood cell production. It is found in red meat, beans, and spinach.
- Vitamin B12: Vital for the formation of red blood cells. Found in meat, eggs, and dairy products.
- Folic Acid: Important for cell growth and replication. Found in leafy greens, beans, and citrus fruits.
Regular exercise, avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals, and refraining from smoking can also help maintain bone marrow health.





One Comment