Symptoms Side Effects of Constipation : Prevention & More
Side Effects of Constipation : Constipation is a common gastrointestinal issue that affects people of all ages. It is generally characterized by infrequent bowel movements, difficulty passing stool, or a sensation of incomplete evacuation.
While it might seem like a minor inconvenience to some, chronic constipation can lead to significant discomfort and health issues. This article delves into the symptoms and side effects of constipation to provide a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
Understanding Constipation
Before diving into the symptoms and side effects, it’s essential to understand what constitutes constipation. Medically, constipation is often defined as having fewer than three bowel movements per week. (Symptoms of constipation in adults)
However, the frequency of bowel movements can vary significantly among individuals, and what is normal for one person may not be for another. Therefore, constipation is also characterized by the difficulty or straining during bowel movements, hard or lumpy stools, and a feeling that not all stool has passed.
Symptoms of Constipation (Constipation danger signs)
Constipation manifests through various symptoms, some of which are directly related to bowel movements, while others are more systemic. The primary symptoms include:
1. Infrequent Bowel Movements
One of the most obvious signs of constipation is having fewer bowel movements than usual. For some, this might mean going several days without a bowel movement, while for others, it could be less frequent than their normal routine.
2. Hard or Lumpy Stools
When stools remain in the colon for an extended period, they tend to become hard and lumpy. This can make them difficult to pass and can lead to discomfort or pain during bowel movements.
3. Straining During Bowel Movements
Excessive straining to pass stools is a common symptom of constipation. This often occurs when stools are hard and dry, making them more challenging to expel from the body.
4. Feeling of Incomplete Evacuation
Many individuals with constipation experience a sensation of incomplete evacuation even after having a bowel movement. This feeling can be frustrating and uncomfortable, as it may seem like there’s still stool left in the rectum.
5. Abdominal Pain and Discomfort
Constipation can cause various forms of abdominal discomfort, including pain, bloating, and cramping. This discomfort is often due to the build-up of stool in the colon, which can lead to a sensation of fullness or pressure.
6. Reduced Appetite
A loss of appetite can be a symptom of constipation, particularly when bloating and abdominal discomfort are present. Feeling full or uncomfortable can decrease the desire to eat.
7. Nausea
In some cases, severe constipation can lead to nausea. This is typically due to the slow movement of food and waste through the digestive tract, which can cause a build-up of gas and discomfort.
8. Rectal Blockage or Obstruction
Feeling like there is a blockage in the rectum can be a sign of constipation. This sensation is often accompanied by the need to use manual maneuvers, such as pressing on the abdomen or using a finger to remove stool, to have a bowel movement.
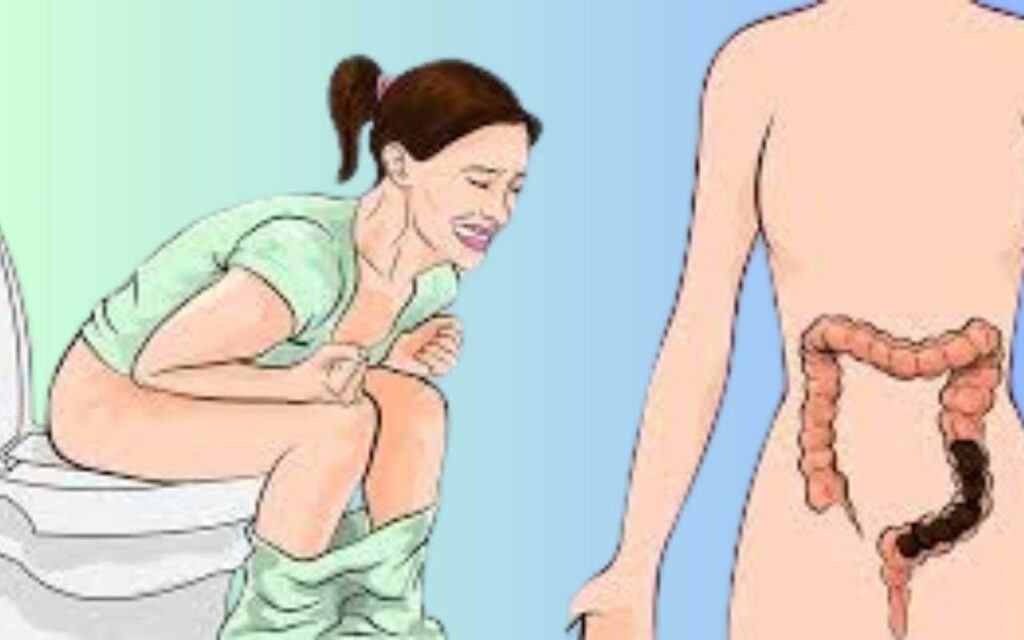
Side Effects of Constipation
Chronic constipation can lead to several side effects, some of which can have significant implications for an individual’s health and quality of life. These include:
- Hemorrhoids: Straining during bowel movements can cause hemorrhoids, which are swollen veins in the rectum or anus. Hemorrhoids can be painful and may bleed during bowel movements.
- Anal Fissures: Passing hard stools can cause small tears in the lining of the anus, known as anal fissures. These can be extremely painful and may also bleed.
- Rectal Prolapse: Chronic straining can lead to rectal prolapse, a condition where a part of the rectum protrudes through the anus. This condition can require surgical intervention.
- Fecal Impaction: Severe constipation can lead to fecal impaction, where a large mass of stool becomes stuck in the colon or rectum. This can be a medical emergency and often requires intervention by a healthcare professional.
- Colonic Diverticulosis: Chronic constipation is associated with the development of diverticula, which are small pouches that can form in the walls of the colon. These pouches can become inflamed or infected, leading to a condition known as diverticulitis.
- Increased Risk of Colorectal Cancer: Some studies suggest that chronic constipation may be associated with an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer. This is thought to be due to the prolonged exposure of the colon to carcinogenic substances in the stool.
- Psychological Impact: Chronic constipation can also have a significant psychological impact. The discomfort and distress associated with the condition can lead to anxiety, depression, and a reduced quality of life. The social stigma and embarrassment associated with bowel issues can further exacerbate these feelings.
- Impact on Daily Life: The symptoms and discomfort associated with constipation can significantly impact an individual’s daily life. Activities may be limited due to pain or the need to be near a bathroom, and the overall well-being can be affected.
- Physical Discomfort and Pain: (Where is constipation pain felt) One of the most immediate side effects of constipation is physical discomfort. Individuals often experience bloating, abdominal pain, and cramping. The sensation of a full, heavy abdomen can be distressing and can interfere with daily activities. Straining to pass hard stools can also cause pain and discomfort, potentially leading to hemorrhoids, which are swollen blood vessels in the rectal area that can become painful and bleed.
- Long-term Health Risks: While occasional constipation is usually not serious, chronic constipation can lead to more significant health issues. Prolonged straining can weaken the pelvic floor muscles, which can contribute to pelvic organ prolapse, a condition where the pelvic organs slip out of place. In severe cases, chronic constipation can lead to fecal impaction, a condition where a large mass of stool becomes stuck in the colon or rectum, requiring medical intervention.
What Foods Helps To Repair Kidneys : Foods & Diet Plan
Causes of Constipation
Understanding the causes of constipation can help in its prevention and management. Common causes include:
- Dietary Factors: A diet low in fiber, inadequate fluid intake, and excessive consumption of processed foods can lead to constipation.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Regular physical activity helps stimulate intestinal function. A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to constipation.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as painkillers, antacids, antidepressants, and iron supplements, can cause constipation as a side effect.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diabetes, hypothyroidism, and neurological disorders can contribute to constipation.
- Ignoring the Urge to Go: Delaying bowel movements can lead to harder stools and reduced urge over time, contributing to constipation.
- Aging: As people age, bowel movements can become less frequent and more challenging due to decreased muscle tone and slower metabolism.
Management and Prevention (Constipation treatment)
Effective management and prevention of constipation involve lifestyle and dietary changes, along with medical interventions when necessary. Key strategies include:
- Increasing Fiber Intake: A diet high in fiber from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can help prevent constipation. Fiber adds bulk to stool and makes it easier to pass.
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids, particularly water, helps keep stool soft and easier to pass.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity stimulates intestinal function and can help prevent constipation.
- Establishing a Routine: Regular bowel habits, such as setting aside time each day for bowel movements, can help.
- Responding to the Urge: Not delaying when the urge to have a bowel movement arises can prevent stool from becoming hard and difficult to pass.
- Medication Review: If constipation is related to medications, consulting a healthcare provider to adjust the dosage or switch to a different medication may help.
- Over-the-Counter Remedies: Laxatives, stool softeners, and fiber supplements can be used to manage constipation, but they should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid dependency and other side effects.
- Constipation medicine : Stimulants – These medications, such as bisacodyl (Correctol, Dulcolax Laxative) and sennosides (Senokot, Ex-Lax, Perdiem), tighten the intestinal walls to help move stool.
Conclusion
Constipation is more than just an inconvenience; it can lead to significant health issues and impact the quality of life. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the potential side effects are crucial for early intervention and effective management. Through dietary changes, increased physical activity, and proper medical care, individuals can prevent and manage constipation, leading to better overall health and well-being. If constipation persists despite these measures, it is essential to seek medical advice to identify and treat any underlying causes.





One Comment